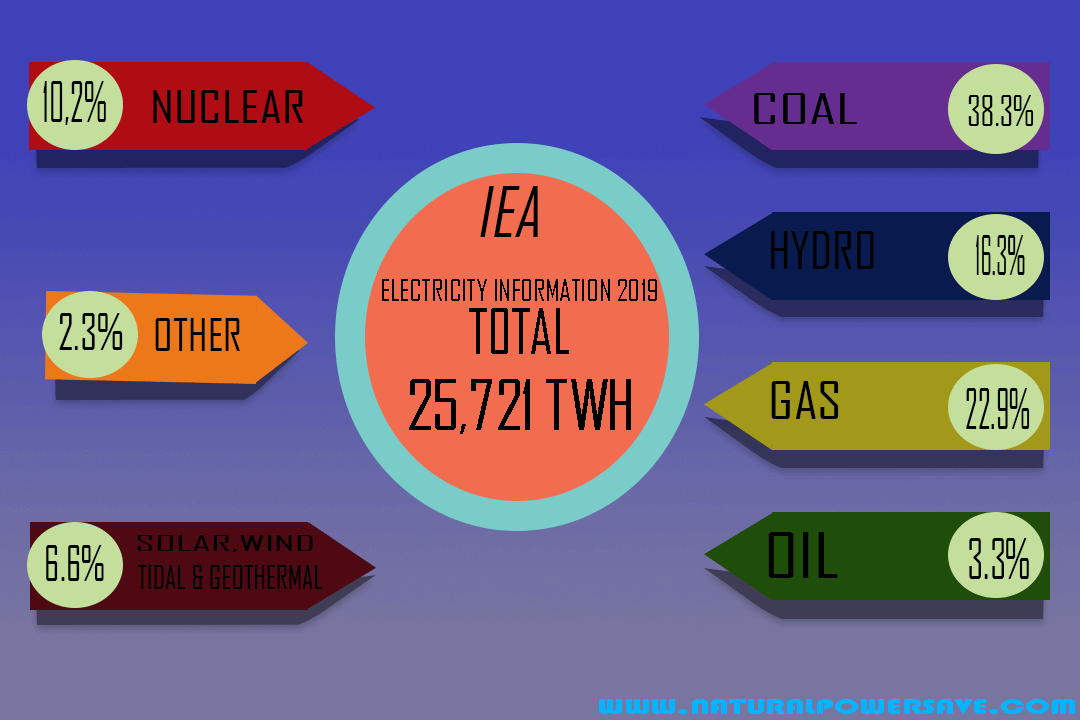
While nuclear power seems to be an excellent way to generate enough energy to sustain all of Earth’s inhabitants, we should dive deep into nuclear energy pros and cons to determine if it’s a sustainable option. One of the biggest challenges we face today is creating energy resources without contributing to our planet’s decline.
Despite the initial thought-train that most people have about nuclear energy, it’s important to distinguish between nuclear energy pros and cons. This dissecting will help us make an informed decision of its use as an alternative source of energy in areas where other sustainable resources don’t meet the needs of ever-increasing populations.
What is Nuclear Energy and How Does It Work
To evaluate nuclear energy’s pros and cons, it’s essential to understand what nuclear energy is and how it works.
What is Nuclear Energy?
Nuclear energy, also called atomic energy, refers to the energy found in the nucleus of an atom. A single atom hosts a tremendous amount of energy in its dense core, and the most widely used atom is uranium. Uranium is popular for the extraction of nuclear power since it’s the only naturally occurring element capable of sustaining a nuclear fission chain reaction.
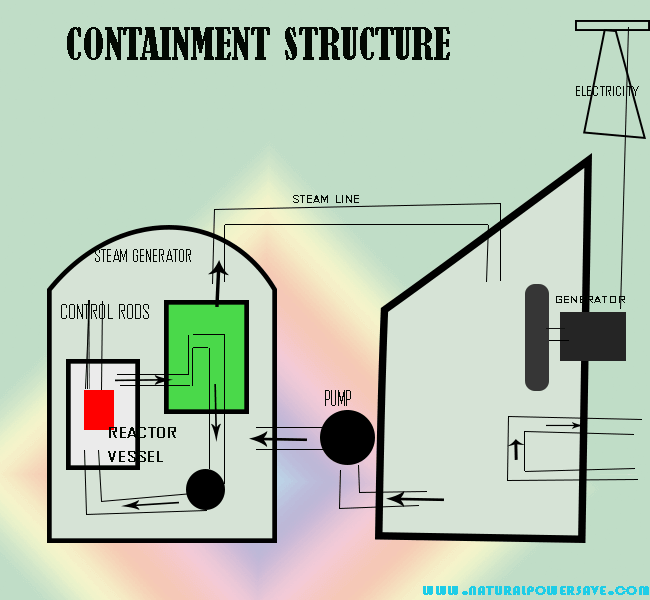
How Does Nuclear Energy Work?
To release energy from an atom for the creation of electricity, a process called nuclear fission is set in motion. Nuclear fission splits the nucleus of an atom, which in turn produces heat that is converted into steam within a nuclear reactor. This steam initiates blades connected to a turbine to turn, which then drives a generator to produce electricity.
Nuclear Energy Pros and Cons
The below table gives a quick overview of the advantages and disadvantages of nuclear energy.
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
Low Operation Costs |
High Initial Costs |
|
Low Carbon Emissions |
Nuclear Meltdowns |
|
Not Intermitted |
Nuclear Waste |
The Advantages of Nuclear Energy Explained
Low Operation Costs: The expenses related to running a nuclear power plant is relatively low. Uranium is a low-cost fuel source producing tremendous amounts of energy, compared to other sources such as gas and goal. Since operational and maintenance costs are low, sufficient funds are available for waste management, with little impact on the price of electricity generated. In conclusion, unlike fossil fuels, nuclear energy also faces a low risk of inflation.
Low Carbon Emissions: This fact is probably worth listing under the best advantages of nuclear energy because nuclear power plants have low greenhouse gas emissions, making it an environmentally friendly source of energy when considering the impact of its production.
Not Intermitted: Unlike renewable energy sources (wind and the sun), nuclear power is not intermittent, which makes it highly reliable.
The Disadvantages of Nuclear Energy Explained
High Initial Costs: Costs relating to the construction of a nuclear plant can amount to billions of dollars, making the initial start-up cost steep. Many nations don’t want to invest in nuclear plants due to their high start-up cost and the time-consuming construction process associated with them.
Nuclear Meltdowns: Small mistakes can lead to disastrous accidents despite the safety measures at nuclear plants. The effects of a nuclear meltdown can be devasting on both the environment and local inhabitants of an area. Compared to other sources of energy, nuclear power is hazardous, and although accidents aren’t a daily occurrence, we should never forget the history of such.
Nuclear Waste: Even though nuclear plants have a low carbon footprint, they generate a large amount of nuclear waste. When this radioactive waste isn’t stored correctly, it pollutes the environment and can take hundreds of years to reach a level of safety that is adequate for human exposure. Currently, the best solution is to seal nuclear waste in secure containers and store it underground where environmental contamination is limited.
Other Uses of Nuclear Energy
Although there are disadvantages of nuclear energy relating to the environment and human exposure, nuclear energy can be used for more than electricity generation when used in conjunction with developing technology.
In some countries, technology is implemented to apply nuclear energy to the agriculture industry. Here, nuclear technology relies on the use of isotopes and radiation to enhance the productivity of food chains in the following ways:
- Irrigation practices are improved to conserve land and water resources.
- Fertilizers are tagged to determine plant usage of nutrients.
- Food safety is ensured by combating pests and diseases.
- Crop and livestock production is increased.
General exposure to humans can indeed be harmful, but the medical world has determined that minimal amounts of radiation can be utilized to benefit medical treatments. Nuclear research has suggested the following:
- Nuclear medicine can serve as a powerful diagnostic tool.
- Nuclear technology can be used to treat cancer, blood imbalances, and hyperthyroidism.
- Gamma rays can sterilize medical equipment such as syringes, burn dressings, surgical gloves, and heart valves.
The Verdict – Pros and Cons of Nuclear Energy
Merely taking an economic approach, it’s clear why nuclear energy is considered a good electricity source. Its low operation costs and reliability can’t be ignored, though we need to keep in mind that it’s not a renewable energy source. However, as technology improves, more knowledge is gained, and resources are geared towards finding ways to make nuclear energy a more sustainable source of power. Like with any other source of energy, there will always be pros and cons of nuclear energy. The key is to outweigh the disadvantages exponentially.