Biomass energy is a renewable energy source that has been used since the first generation of humans. Biomass energy has a number of advantages and disadvantages which we will explore in this article.
Biomass itself is a renewable material from organic sources, namely plants and animals. In the mid-1800s, biomass is the primary source of energy consumption in the United States. Many countries, mainly developing ones, still use biomass as an essential energy source for cooking and heating. Due to its low carbon dioxide emission, developed countries are beginning to implement biomass fuels for transportation and electricity.
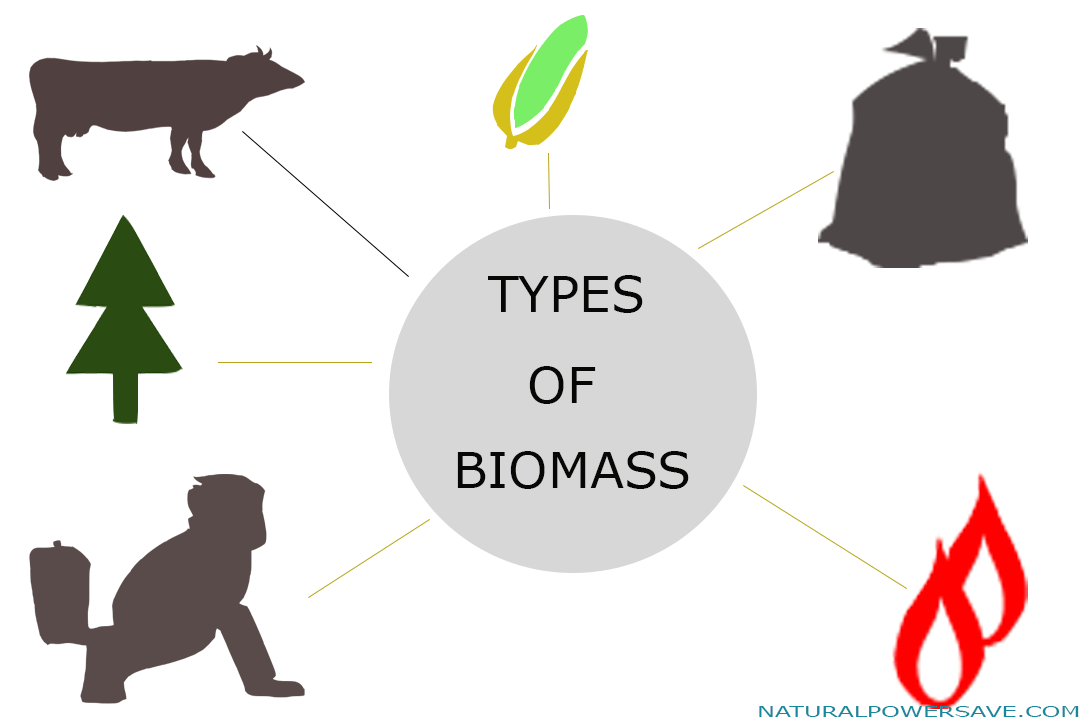
There are several primary sources of biomass energy:
- Wood, including firewood, wood pellets, wood chips, lumber and sawdust, and black liquor.
- Crops such as waste materials, corn, soybeans, sugar cane, and woody plants.
- Biogenic materials, including paper, cotton, wool, and food wastes.
- Manure, both from humans and animals.
Types of Biomass Energy Conversion
There are four ways to convert natural resources into biomass energy. Let us go over them quickly.
Thermal Conversion
The thermal conversion uses heat as the primary catalyst to convert biomass into a usable energy source. This type of conversion is often used to convert dry waste that contains a large percentage of non-biodegradable compounds.
Chemical Conversion
Chemical conversion of biomass allows us to produce solid, liquid, and gaseous fuels from waste. The converted energy from chemical conversion can be a substitute for almost any kind of fossil fuel.
Biochemical Conversion
Biochemical conversion of biomass uses the enzymes found in bacteria and microorganisms to turn the biomass through anaerobic digestion, fermentation, and composting.
Biomass Energy Advantages and Disadvantages
Biomass energy is a renewable source, and therefore it offers a set of advantages. However, it still comes with certain drawbacks.
Biomass Advantages
Being renewable and easy-access energy sources, biomass offers many benefits that fossil fuels can’t provide.
Renewable Energy
Biomass energy is available in abundance throughout the world. The organic materials that can be converted into biomass energy are infinite since we produce waste such as garbage, wood, and manure every day.
Reduce waste
Converting solid waste into biomass energy by burning them, the amount of garbage in landfills will decline significantly (around 60-90 percent). In turn, converting solid waste to biomass energy will reduce the cost of landfill disposal and enables more land to be used for something else.
Carbon Neutral
Biomass fuels are a natural byproduct of photosynthesis, and therefore they only release an average amount of carbon to the atmosphere. This amount of carbon is the same as the amount that plants absorb over their life cycle.
Reduces Need for Fossil Fuels
Other than its limited availability in nature, fossil fuels also release a more considerable amount of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Biomass energy helps reduce this environmental impact by providing an alternative with a lower carbon dioxide production.
High Profitability for Producers
Since the sources are mostly waste, biomass energy has a higher profit margin compared to fossil fuels. Of course, this point only applies to biomass power plants and those who profit from them. But this also means that biomass energy price is cheaper for the general public as well.
Biomass Disadvantages
With all its benefits, biomass also comes with specific weaknesses when used as an energy source.
Cost
Operating a biomass energy plant can be costly compared to running a traditional power generator. The main factors that drive the cost up are the required storage space for the biomass energy source and the numerous different processes to convert the biomass into usable energy.
Greenhouse Gas
Even though it emits a smaller amount of carbon dioxide, biomass energy still contributes significantly to the greenhouse gas being released into the atmosphere. We can always avoid carbon dioxide emissions using other renewable sources such as wind turbines and solar panels.
Inefficient
Biomass energy is not as efficient as fossil fuels in terms of its conversion rate. In some cases, the energy you’d need to convert the biomass is more significant than the biomass energy output. To crank up its efficiency, it needs a mixture of petrol and diesel – which means it’s not ready for mass usage just yet.
Environmental Impact
One of the sources of biomass energy is wood – which we can get from forests. Using biomass energy on a larger scale can lead to deforestation. Even if wood waste is abundant, biomass fuels’ inefficiency might result in more wood than just the scraps.
In some cases where biomass plants grow monoculture crops, there are also risks of soil nutrient stripping, impacting the biodiversity negatively.
Conclusion
Biomass energy is indeed a promising alternative to fossil fuels, but it still has flaws that we need to overcome before using it on a larger scale. Many countries have already found the perfect use case scenarios for biomass energy. Many more countries will likely adapt to using biomass energy into their energy source planning soon.


Trackbacks/Pingbacks